Introduction
More and more organizations are increasingly relying on Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) and document automation tools to streamline workflows, reduce manual effort, and improve data accuracy.
From invoices and purchase orders to contracts and quality checklists, the volume and complexity of documents that companies handle are growing exponentially. As a result, tools that can quickly extract, process, and structure this information have become critical to operational efficiency.
Among the many solutions available, Nanonets is a popular choice for AI-powered OCR and data extraction. Its platform allows users to automate document workflows and extract structured data from a variety of sources. However, while Nanonets has proven useful for standard use cases, it faces notable limitations.
Users often encounter challenges related to accuracy, especially with complex or handwritten documents, flexibility in adapting to changing document formats, and cost, which can escalate quickly under a block-based pricing model. Additionally, Nanonets’ closed, black-box system limits visibility and control over the underlying AI models, making it harder for teams to customize or optimize extraction workflows.
This article explores how Unstract, a modern and AI-native alternative, is designed to address these challenges. Unstract offers a prompt-driven, modular platform that supports multi-service text extraction, human-in-the-loop validation, and seamless deployment through ETL pipelines and APIs. Its architecture is built for flexibility, scalability, and transparency, giving organizations greater control over their document processing workflows.
About Nanonets
Nanonets is an AI-powered platform designed to automate document processing and data extraction. It combines Optical Character Recognition (OCR) with machine learning to help businesses convert unstructured documents, like invoices, forms, contracts, and receipts; into structured, machine-readable data. By automating these workflows, Nanonets aims to reduce manual data entry, minimize errors, and accelerate business operations.
Strengths
Nanonets has several advantages that make it appealing for certain use cases:
- Pre-built Models: The platform offers ready-to-use models for common document types, enabling quick adoption without extensive setup.
- Integrations: Nanonets provides connections to popular tools and services, such as Google Drive, Zapier, and cloud storage solutions, allowing extracted data to flow seamlessly into existing workflows.
- Ease of Use for Structured Documents: For relatively simple and standardized documents, Nanonets allows users to quickly set up extraction rules and obtain accurate results.
Limitations
Despite its strengths, Nanonets has several limitations that can hinder more complex or large-scale document processing initiatives:
- Manual Template-Based Extraction: Users often need to define extraction areas by drawing borders and boxes around data fields. This approach is time-consuming, error-prone, and not easily scalable. If the document layout changes, the extraction setup must be redone.
- Cost Scales with Usage: Nanonets uses a block-based pricing model, where every document processed counts toward your usage quota. For high-volume workflows, costs can escalate quickly.
- Limited Control Over AI Stack: The platform operates as a closed system, giving users little flexibility to choose the underlying OCR engine, LLM, or AI models. This restricts customization and optimization.
- Difficulty with Complex or Unstructured Documents: Documents with irregular layouts, handwritten text, or mixed content often yield inconsistent results, reducing the platform’s reliability for advanced use cases.
Overall, while Nanonets remains a strong choice for standard, structured documents, its limitations become apparent when handling complex, unstructured, or high-volume workflows. These gaps create an opportunity for a more flexible, AI-native alternative like Unstract, which is designed to address these challenges.
Trying Out Nanonets
To begin evaluating Nanonets, start by creating a free trial account. Visit the official signup page at https://app.nanonets.com/#/signup and register using your email address.
The onboarding process is quick and after verifying your email, you’ll gain access to the Nanonets dashboard, where you can begin exploring its pre-built models, uploading documents, and testing its extraction features.
The first test document that we will test is a multi-row, multi-column table that includes checkboxes, mixed text alignment, and varying cell structures:
Test document 1 → Download
The second document is a handwritten, scanned page: Test document 2 → Download
With the documents ready, head to the Nanonets dashboard to begin the actual extraction tests.
OCR Within Nanonets
First, we will understand how Nanonets handles OCR in general. Its extraction engine is designed for straightforward, structured documents, but performance can vary significantly depending on layout complexity, handwriting, or non-standard formats.
Document With Table And Checkboxes
On the main interface, look for and select the “Instant Training Model” option. This is Nanonets’ guided setup for quickly creating a model by uploading sample documents and defining the fields you want to extract:
Inside it, select “Instant Training Model – Extract Data”, which allows you to quickly test the platform’s OCR and structured data extraction by uploading a file:
After uploading this first test document, a table with checkboxes, Nanonets automatically processes the file using its OCR and extraction models:
When we review the OCR results for the first test document, we can see that Nanonets’ initial recognition correctly identified some of the text fields and the overall table structure. It was able to detect rows, columns, and the textual content within the cells.
However, the platform completely missed the checkboxes, failing to recognize them as distinct elements or actionable fields.
As a result, additional manual corrections or template adjustments would be required to accurately capture all the data, reducing efficiency and scalability for documents that combine text with form elements like checkboxes
Handwritten Scan
Next, we tested Nanonets using the second document, a scanned handwritten page. This document contains freeform text, mixed handwriting styles, and varying line spacing, making it a more challenging case for OCR:
The results show that Nanonets struggled to accurately recognize the handwritten content. While some of the more clearly written words were detected correctly, many characters were misread, and entire sections of the text were either partially captured or completely missed.
Extracting Data From Documents
Once the text has been successfully extracted using OCR, the next step is transforming that raw text into structured, usable data.
Document With Table And Checkboxes
To test structured data extraction in Nanonets, we created a new workflow project and uploaded one of the test documents. Nanonets requires users to manually define the fields they want to extract:
This process involves drawing borders and boxes around each data point in the document and labeling them appropriately. For simple documents, this can be manageable, but for complex tables, scanned forms, or documents with multiple sections, the task quickly becomes time-consuming and tedious.
Within the workflow project in Nanonets, you have the option to add new fields in the AI section to automate extraction for specific data points:
However, even when adding a new field, you still need to manually define a box around the field on the document and provide a label:
The AI then uses this template to extract the same field across similar documents automatically.
Handwritten Scan
After testing the first document, we set up a new workflow for the second document, which contains handwritten, scanned text. As with the first workflow, Nanonets requires a manual setup, as each data field you want to extract must be defined with a labelled box:
For handwritten content, this process becomes even more challenging. The AI relies on the boxes to locate and interpret text, but variations in handwriting, line spacing, and scan quality can make the extraction less accurate
After processing the documents in Nanonets, the next step is to export the extracted data. While the platform allows you to download results, the export options are somewhat limited:
Common formats include CSV, Excel, and integrations with third-party apps, but there is no direct option to export structured data as JSON.
One of the major limitations we observed while using Nanonets is that the workflow setup is clunky and requires extensive manual tweaking:
Even after manually creating the workflow and adjusting the extraction regions, Nanonets still requires you to manually define every field you want to export. Instead of automatically detecting or suggesting structured fields based on the document content, users must name each field, map it, and ensure the correct bounding box is linked to it.
For HITL (Human-in-the-loop), the options are mostly limited to having a human review the entire document. There are no configurable ratios, thresholds, or rule-based triggers to selectively route only uncertain fields for validation.
Additionally, when trying to set up an integration using the official API documentation
(https://docs.nanonets.com/docs/integrate-via-api), we found that much of the information is outdated or inaccurate.
Observations
Working hands-on with Nanonets reveals several friction points that become apparent as soon as you move beyond simple, well-structured documents. The platform offers useful baseline automation, but its workflow quickly becomes cumbersome when dealing with real-world variability.
Manual setup is required at nearly every stage, when creating fields, drawing bounding boxes, adjusting layouts, and re-training for even small changes in document structure. This slows down experimentation and makes it difficult to handle diverse file types without repeated configuration work.
Additionally, the limited Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) functionality means there’s no smooth way to validate low-confidence predictions or correct mistakes using reviewers. Instead, the user must step in manually and repeatedly to fix outputs or redefine fields.
Finally, integrations that should streamline export and automation are hindered by outdated documentation (e.g., the API integration guide), resulting in failed or inconsistent setups.
Overall, the system demands significant tweaking and rework, especially for complex layouts, handwritten documents, or documents with checkboxes; and this manual burden compounds as document formats evolve.
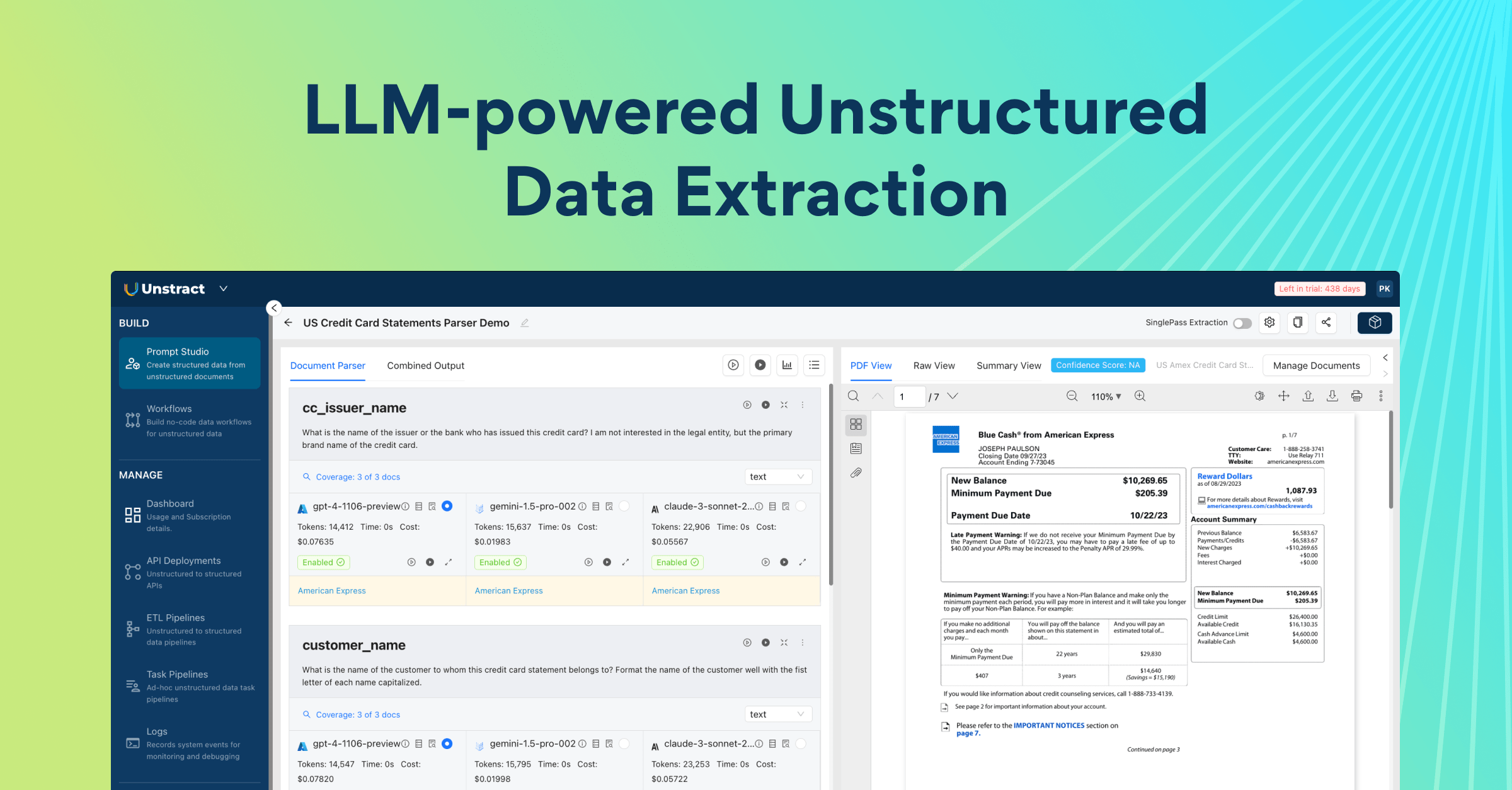
Introducing Unstract
Unstract is a modern, AI-native, open-source platform designed to reimagine document processing and structured data extraction. Unlike traditional IDP tools, which often rely on rigid templates, manual training, or closed proprietary models, Unstract is built from the ground up to leverage large language models (LLMs), vector databases, and modular OCR services to handle a wide range of document types; structured, semi-structured, and completely unstructured.
At its core, Unstract aims to solve the common pain points faced by users of platforms like Nanonets: the need for manual template setup, the high cost of scaling, limited control over AI models, and difficulty processing complex or handwritten documents. By providing a flexible, prompt-driven approach, Unstract enables teams to extract data efficiently and accurately without extensive setup or technical expertise.
From data extraction to validation and deployment, the platform is designed to fit seamlessly into existing IT infrastructure. Its architecture supports self-hosted deployments for organizations with strict security or compliance requirements, as well as cloud-based deployments for teams seeking speed and ease of use.
With built-in human-in-the-loop (HITL) capabilities, multiple users can review and validate extracted data by defining rules to ensuring quality and consistency at scale. The system also supports ETL pipelines and API-first deployments, making it suitable for enterprises, SaaS applications, and data-driven organizations that require real-time access to structured information from diverse document sources.
Unstract is not just a tool, it’s a complete document automation ecosystem that combines the power of modern AI, flexible integration, and user-friendly design to enable smarter, faster, and more accurate document workflows.
Core Advantages Over Nanonets
- Prompt Studio: Extract structured data using simple English prompts, no training or template setup required. Prompts are intuitive and easily adaptable to changing document formats, making workflows faster and more scalable.
- Multi-Service Text Extraction: Choose from specialized OCR solutions like LLMWhisperer or bring your own LLMs and vector databases. This flexibility improves accuracy and allows cost-efficient extraction tailored to your needs.
- Flexible AI Stack: Modular design lets you select OCR engines, LLMs, embeddings, and databases. This eliminates vendor lock-in and gives full control over performance, scalability, and cost.
- Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Review: Low-confidence extractions can be routed to reviewers for validation, ensuring consistent, high-quality data output.
- ETL Pipelines & Pre-Built Connectors: Automatically deliver extracted data to cloud storage, databases, or analytics platforms, enabling end-to-end workflow automation without additional engineering.
- API-First Deployment: Deploy extraction workflows as APIs to provide real-time structured data access across teams, applications, and services.
Trying Out Unstract
To get started, visit the Unstract website and sign up for a free account. The registration process is quick and gives you immediate access to Unstract’s core tools, including Prompt Studio and LLMWhisperer.
Each new account includes a 14-day free trial and 1 million LLM tokens, providing everything you need to start building and testing your own document extraction pipelines right away.
OCR with LLMWhisperer
Unstract offers access to LLMWhisperer, a next-generation OCR engine designed to handle messy, complex, and real-world documents with far greater accuracy.
LLMWhisperer can be tested directly in the browser via the official playground at https://playground.llmwhisperer.unstract.com/.
This makes it easy to upload documents, including handwritten scans, noisy PDFs, checkbox forms, or irregular tables, and instantly see how the AI interprets them.
Document With Table And Checkboxes
By uploading this document to the LLMWhisperer playground, we can immediately see how effectively the model parses table structures, identifies checkbox states, and maintains contextual accuracy throughout the extraction:
The table entries are accurately identified, the checkboxes are correctly recognized, and the overall structure of the document is preserved, making the extracted output clean, reliable, and ready to be used directly in downstream pipelines.
Handwritten Scan
Handwritten documents are typically the most challenging for traditional OCR systems, especially when the text varies in style, spacing, or scan quality. With LLMWhisperer, however, these limitations are significantly reduced:
The overall layout is preserved, all handwritten text is accurately detected, and even the embedded table is recognized with its structure intact. This demonstrates once again how LLLMWhisperer delivers exceptional OCR performance, enabling seamless use of the extracted data in automated pipelines.
Extracting Data From Documents
Once documents have been processed with OCR, the next step is to test workflow-based extraction in Unstract. The platform combines accuracy-enhancing tools, multi-service text extraction, and flexible deployment options to create a fully automated pipeline.
Key features include:
- LLMchallenge: Ensures extracted data is accurate by automatically validating and correcting uncertain fields.
- Multi-Service Text Extraction: Choose between LLMWhisperer, custom LLMs, or vector databases for optimal accuracy and cost efficiency.
- ETL & API Integration: Easily connect extracted data to databases, analytics platforms, or deploy workflows as APIs for real-time processing.
Once logged in to Unstract, open Prompt Studio and create a new project for your document(s). Navigate to the Manage Documents section to upload the files you want to process. After uploading, you can define prompts that describe the exact data fields you want to extract, such as names, dates, totals, or checkbox selections.
In Unstract, prompts act as instructions for the AI, specifying what to extract and how to structure the output. This ensures results match your schema and maintain consistency across multiple documents. Unlike Nanonets static extraction, where the system guesses fields based on its internal model, Unstract gives you full control over extraction logic, allowing you to enforce data types, adjust output structure, and refine prompts as needed.
Document With Table And Checkboxes
For this document, we will create a generic prompt to extract the data from the table:
Retrieve the information from the table, organizing each column with the corresponding name, marked by the (). Return it as a JSON with a list of rows with the columns inside.Running the prompt:
You can see that even with a generic prompt, the AI correctly matches the columns, captures the values from the checkboxes, and organizes the data neatly into rows.
The extracted data is now ready for downstream processing.
Let’s take a look at the full JSON output:
[
{
"All other illnesses": false,
"Case no.": "3443",
"Date of injury or onset of illness": "24 month/day",
"Days away from work": "32 days",
"Describe injury or illness, parts of body affected, and object/substance that directly injured or made person ill": "First degree burns in arms yard laceration in the neck",
"Employee's name": "Roger Smith",
"Hearing loss": false,
"Injury": true,
"Job title": "Engineer",
"On job transfer or restriction": "24 days",
"Poisoning": false,
"Respiratory condition": false,
"Skin disorder": false,
"Where the event occurred": "Dock yard"
},
{
"All other illnesses": false,
"Case no.": "8932",
"Date of injury or onset of illness": "2 / 4 month/day",
"Days away from work": "16 days",
"Describe injury or illness, parts of body affected, and object/substance that directly injured or made person ill": "Fractured right leg",
"Employee's name": "William potter",
"Hearing loss": false,
"Injury": true,
"Job title": "Engineer",
"On job transfer or restriction": "",
"Poisoning": false,
"Respiratory condition": true,
"Skin disorder": false,
"Where the event occurred": "Dock yard"
},
{
"All other illnesses": false,
"Case no.": "767",
"Date of injury or onset of illness": "24 month/day",
"Days away from work": "",
"Describe injury or illness, parts of body affected, and object/substance that directly injured or made person ill": "",
"Employee's name": "Simon Dawes",
"Hearing loss": false,
"Injury": true,
"Job title": "Engineer",
"On job transfer or restriction": "",
"Poisoning": false,
"Respiratory condition": false,
"Skin disorder": false,
"Where the event occurred": "Dock"
}
]
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Review
One of Unstract’s most powerful capabilities is its human-in-the-loop (HITL) review system, which lets users verify and correct uncertain extractions in real-time. HITL ensures that challenging cases; such as handwritten notes, irregular or skewed tables, noisy scans, or low-confidence fields; are captured with maximum accuracy.
Within any workflow, you can seamlessly integrate HITL alongside downstream actions. For example, you can configure a database connector to automatically receive processed data while still routing selected documents for manual validation:
Unstract gives you full control over how the review process behaves. You can define what percentage of documents require manual review, set confidence thresholds, and specify validation rules for any field. The platform provides multiple configuration options, allowing teams to fine-tune their quality checks with precision.
By blending automation with targeted human oversight, Unstract’s HITL workflow delivers the ideal balance between speed and reliability, making it an excellent choice for organizations that demand both scalability and high-accuracy document processing.
Handwritten Scan
For this document, we will create a prompt to extract the table data as well.
Extract the information from the table that contains the gross weight, do extract all the columns. Return it as a JSON list with rows and inside the columns with the corresponding names.Running the prompt:
Even with minimal guidance, the AI correctly extracted the columns and rows, accurately recognizing the handwritten text from a slightly skewed scan.
Let’s take a look at the resulting JSON:
[
{
"Chargeable Weight": "30kg",
"Commodity Item No": 3,
"Gross Weight kg": "30kg",
"Gross Weight lb": null,
"Nature and Quantity of Goods": "News print Paper",
"No. of Pieces": 3,
"Rate Charge": "$2",
"Total Charge": "$60"
},
{
"Chargeable Weight": "30 kg",
"Commodity Item No": null,
"Gross Weight kg": null,
"Gross Weight lb": "72",
"Nature and Quantity of Goods": "Package Paper.",
"No. of Pieces": 5,
"Rate Charge": "$3",
"Total Charge": "$60"
},
{
"Chargeable Weight": "10kg",
"Commodity Item No": null,
"Gross Weight kg": null,
"Gross Weight lb": "75",
"Nature and Quantity of Goods": "Print Ink Solution",
"No. of Pieces": 3,
"Rate Charge": "$6",
"Total Charge": "$70"
}
]
Deploying as an API
Deploying to an API is simple, just click the “Deploy as API” button in Prompt Studio. Follow the short, two-step wizard, and the API is live. There’s no manual configuration or additional settings required:
Observations
Testing Unstract with complex documents highlights several practical advantages over traditional template-based systems:
- Faster Iteration: Prompt-based extraction allows for quick adjustments and immediate reprocessing of documents, eliminating the need to redraw boxes or retrain models.
- Reduced Manual Work: Multi-service OCR, schema-driven prompts, and human-in-the-loop validation minimize repetitive tasks, freeing up time for more valuable work.
- Greater Control: Users have full control over extraction logic, data schema, and workflow integration, enabling more accurate and consistent results across varied document types.
Overall, Unstract streamlines document processing, improves accuracy, and provides a flexible, scalable solution for enterprise workflows.
Nanonets vs. Unstract: Key Differences
When choosing a document processing platform, it’s important to look beyond basic OCR capabilities and consider factors like workflow flexibility, accuracy, and integration options.
Below is a detailed comparison between Nanonets and Unstract:
| Feature | Nanonets | Unstract |
|---|---|---|
| Extraction Method | Template-based; requires manually drawing borders and boxes around fields | Prompt Studio: extract structured data using simple English prompts, no manual template setup |
| OCR Accuracy | Limited performance with complex, handwritten, or noisy documents | Multi-service OCR, including LLMWhisperer, ensuring higher accuracy even on challenging inputs |
| Structured Data Extraction | Manual setup, retraining needed for new formats | Instant extraction using adjustable prompts; adapts easily to new document layouts |
| Human-in-the-loop (HITL) | Minimal support for review | Full-featured HITL for validation and quality assurance of uncertain extractions |
| Flexibility / AI Stack | Closed system, limited control over AI models | Modular design: bring your own LLMs, OCR engines, and vector databases |
| Cost Model | Usage-based (block pricing) | Open-source/self-host or cloud deployment → predictable and potentially lower cost |
| ETL & Deployment | Basic integrations | Full ETL pipelines, API-first deployment, and pre-built connectors for servers and analytics platforms |
| Transparency | Black-box AI models | Full visibility into extraction logic and workflow configurations |
| Handling Complex Documents | Struggles with long, unstructured, or intricate formats | Handles long, unstructured, and highly complex documents with ease |
Additional Differentiators:
- Scalable Workflows: No need to redraw extraction boxes for new documents or formats
- Privacy & Compliance: Self-hosted options make it better suited for regulated or sensitive data
- Future-Proof Architecture: Easily integrates with LLMs and vector databases for advanced document automation
Unstract’s modern, AI-native architecture clearly addresses the limitations of traditional template-based platforms like Nanonets, making it a more accurate, flexible, and scalable solution for enterprise document processing.
Unstract, a better Nanonets alternative: What’s next?
Unstract offers a modern, flexible, and AI-native alternative to Nanonets, designed to address the limitations of traditional document processing platforms.
By combining prompt-based extraction, multi-service OCR, and LLM integration, it enables organizations to process complex documents more accurately and efficiently.
The platform’s human-in-the-loop validation ensures high-quality data, while its support for full ETL pipelines and API deployment allows seamless integration into existing workflows and enterprise systems.
For teams looking to streamline document automation, reduce manual effort, and gain full control over their AI-powered extraction workflows, Unstract represents a compelling choice.
By testing Unstract with your own complex documents, you can experience firsthand how its flexible, scalable, and cost-efficient architecture outperforms Nanonets and sets a new standard for intelligent document processing.
Unstract, A better Nanonets Alternative: Related topics to explore